Nov . 07, 2024 12:27 Back to list
Exploring the Charm of a Tiny Artisan Workshop in the Heart of the City
The Rise of Tin Small Factories A Sustainable Solution to Modern Manufacturing
In recent years, the manufacturing landscape has seen a notable shift towards more sustainable and localized production methods. Among various trends, the emergence of tin small factories has garnered significant attention. These small-scale manufacturing units, often powered by renewable energy and employing local craftsmanship, represent a promising solution to the challenges posed by large-scale industrial production. This article explores the concept of tin small factories, their advantages, and their potential impact on society and the economy.
What Are Tin Small Factories?
Tin small factories are essentially compact manufacturing units that primarily focus on creating products using tin and other metals. Unlike traditional factories that require substantial capital investment and vast amounts of space, tin small factories operate on a smaller scale. They can be located in urban neighborhoods or rural areas, leveraging local resources and workforce. The term tin refers not just to the material used, but also symbolizes a return to basics in manufacturing, where simplicity meets efficiency.
Advantages of Tin Small Factories
1. Sustainability One of the most significant advantages of tin small factories is their potential for sustainable production. By utilizing local materials and resources, these small factories can minimize transportation emissions and support local economies. Additionally, many tin small factories are adopting renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, further reducing their environmental footprint.
2. Job Creation The rise of tin small factories has the potential to create numerous job opportunities in the community. These factories often employ local artisans and craftsmen, providing them with stable income and the chance to practice their skills. This focus on local employment can significantly contribute to economic development in areas that may have been overlooked by larger corporations.
3. Customization and Innovation While large factories typically mass-produce standardized items, tin small factories can adapt quickly to changing consumer demands. Their smaller size allows for greater flexibility, enabling them to offer customized products tailored to specific customer needs. This capacity for innovation and personalization can drive creativity and improve customer satisfaction.
4. Resilience to Economic Shifts The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerabilities of global supply chains. Tin small factories, with their localized production, are less susceptible to such disruptions. By focusing on local markets and resources, these factories can adapt more swiftly to economic changes and maintain steady production levels.
tin small factory
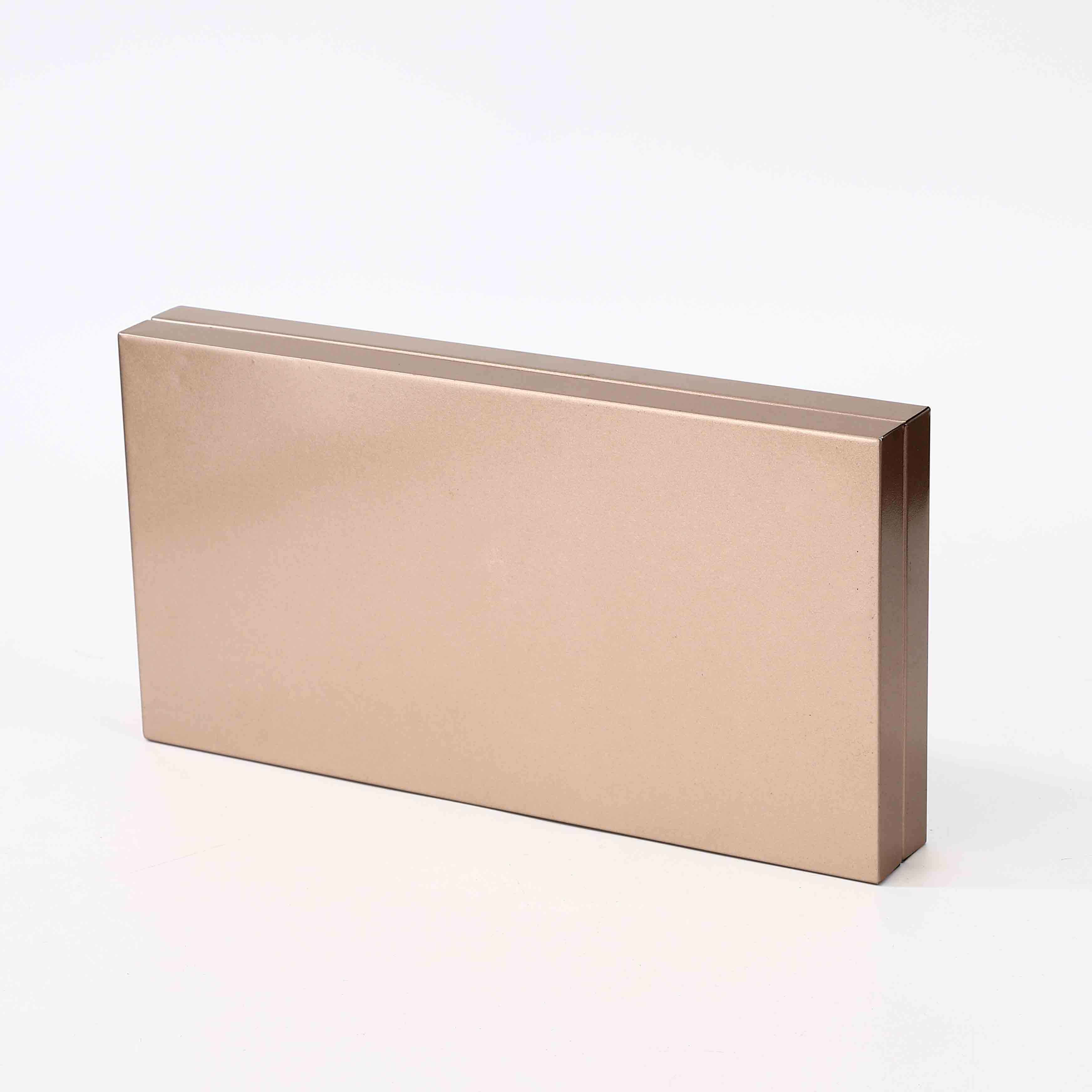

Challenges Facing Tin Small Factories
Despite their potential, tin small factories face several challenges. Access to funding can be a significant hurdle, as many entrepreneurs lack the capital to start and sustain a manufacturing unit. Additionally, while the demand for small-scale, artisanal products is rising, these businesses must compete against larger corporations that can offer lower prices due to economies of scale.
Moreover, there is a need for adequate training and skill development. To maximize their potential, workers must be educated in the latest manufacturing techniques, sustainability practices, and business management skills. Collaboration with local educational institutions and vocational training centers can help address this gap.
The Future of Tin Small Factories
The future of tin small factories looks promising as consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing. With a growing trend towards supporting local businesses, these factories can play a vital role in fostering community resilience and economic stability.
Governments, NGOs, and the private sector must collaborate to create an enabling environment for tin small factories. This can be achieved through policy support, access to financing, and incentives for sustainable practices. By investing in these small-scale industries, society can cultivate a more sustainable and equitable economy.
Conclusion
Tin small factories embody a forward-thinking approach to manufacturing that aligns with the principles of sustainability, local empowerment, and innovation. As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change and economic uncertainty, these small manufacturing units offer a viable solution that benefits both communities and the environment. Embracing the tin small factory movement could pave the way for a brighter, more sustainable future for all.
-
Durable Large Metal Boxes | Top Manufacturers & Suppliers
NewsAug.09,2025
-
Custom Large Metal Box Manufacturers: Durable & Reliable Solutions
NewsAug.08,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers - Custom & Durable Solutions
NewsAug.07,2025
-
Durable Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | AI-Powered Solutions
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Leading Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.04,2025