Sep . 17, 2024 01:41 Back to list
Quality Tin Food Cans Factory | Durable & Reliable Packaging Solutions
The Evolution of Tin Food Can Factories A Testament to Innovation and Sustainability
The history of tin food cans dates back to the early 19th century, marking a significant advancement in food preservation technology. The invention of the canning process, attributed to Nicolas Appert in 1809, laid the groundwork for the development of tin food can factories. Initially designed to provide sustenance for soldiers and sailors during wartime, these cans have evolved into an essential component of the global food supply chain.
The Evolution of Tin Food Can Factories A Testament to Innovation and Sustainability
Automation plays a vital role in contemporary canning operations. The widespread use of conveyor systems and robotic technologies enhances efficiency and minimizes human error. Not only does this ensure consistency in production quality, but it also allows for large-scale manufacturing that meets the ever-increasing demand for canned goods. On average, a state-of-the-art tin can factory can produce thousands of cans per minute, catering to both local markets and international exports.
tin food cans factory
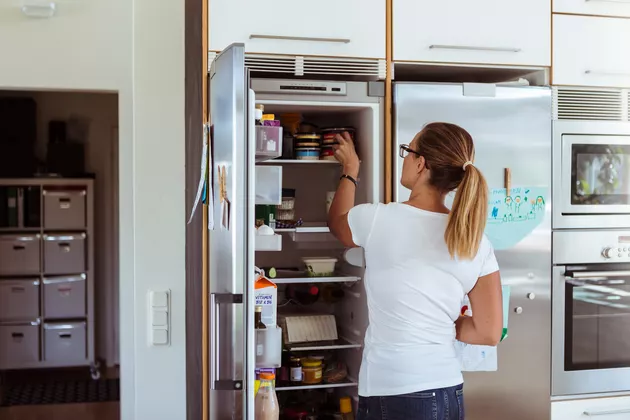

Sustainability has become a focal point in recent years, influencing the operational strategies of tin food can factories. Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as recycling scrap metal and implementing energy-efficient machinery. Tinplate is highly recyclable, making tin cans one of the most sustainable packaging options available. The recycling process requires significantly less energy compared to raw material production, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, the trend toward healthy eating and convenience has propelled the canned food industry to new heights. Today, consumers are presented with a wide array of options, from organic vegetables to ready-to-eat meals. Innovative marketing strategies, including clever packaging, have also played a crucial role in attracting health-conscious buyers.
In addition to transforming the way we preserve food, tin food can factories have had a significant impact on global trade. Countries specialize in different aspects of can production, and international partnerships have emerged to optimize the supply chain. This interconnectedness facilitates the exchange of goods and keeps prices competitive, ultimately benefiting consumers worldwide.
In conclusion, tin food can factories represent a fascinating blend of history, technology, and sustainability. From their inception as a practical solution for food preservation to their current status as a staple in modern diets, the evolution of these factories illustrates the remarkable ingenuity of human innovation. As we move forward, the ongoing commitment to eco-friendly practices will ensure that tin food cans remain a vital and sustainable part of our food systems for generations to come.
-
Durable Large Metal Boxes | Top Manufacturers & Suppliers
NewsAug.09,2025
-
Custom Large Metal Box Manufacturers: Durable & Reliable Solutions
NewsAug.08,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers - Custom & Durable Solutions
NewsAug.07,2025
-
Durable Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | AI-Powered Solutions
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Leading Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.04,2025