Aug . 01, 2024 09:16 Back to list
Exploring the Production Process for 4L Gallons in a Modern Manufacturing Facility
The Impact of 4L Gallons Factory on Sustainable Production and Environment
In recent years, the global community has awakened to the pressing need for sustainable production methods and environmental preservation. Among the innovative solutions emerging in this landscape is the concept of the 4L Gallons Factory—a new paradigm in manufacturing that emphasizes efficiency, resourcefulness, and eco-friendliness. This idea revolves around the production of goods with minimal waste and optimal use of resources, represented symbolically by the 4 liters or 4 gallons measurement.
At its core, the 4L Gallons Factory aims to redefine how we think about resource consumption in manufacturing processes. Traditional factories often operate under outdated models that prioritize volume over sustainability, leading to excessive waste generation and environmental degradation. The concept of a 4L Gallons Factory challenges this norm by focusing on producing goods that meet consumer needs without over-exploiting natural resources. This is achieved by optimizing production processes, utilizing innovative technologies, and adopting eco-friendly practices.
The Impact of 4L Gallons Factory on Sustainable Production and Environment
Water usage is another critical aspect addressed by the 4L Gallons Factory model. Conventional manufacturing often leads to water wastage and pollution. However, factories adhering to this model implement water recycling systems and use minimally invasive processes that significantly reduce water usage. This approach not only conserves a vital resource but also diminishes the ecological impact typically associated with wastewater discharge.
4l gallons factory
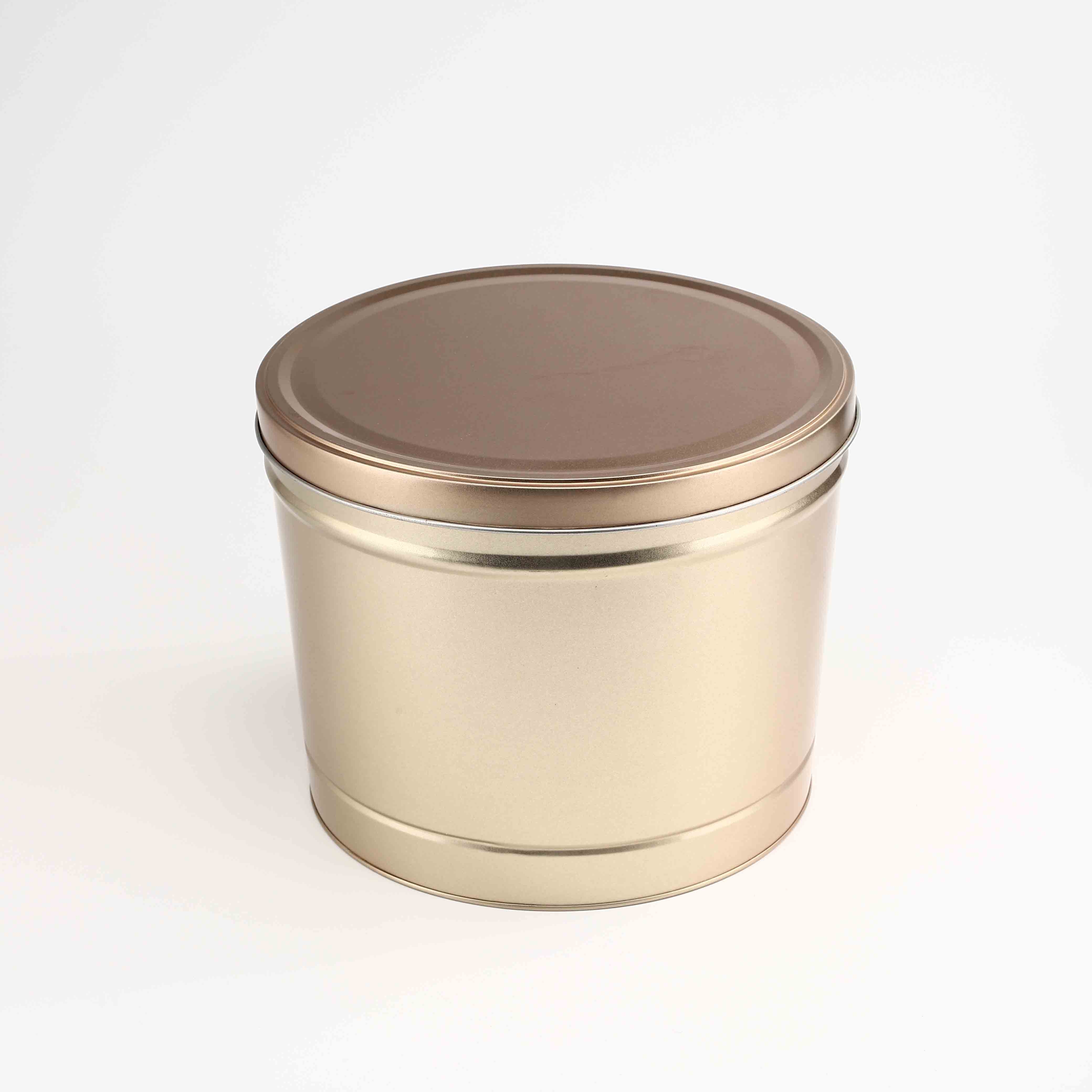

In addition to resource efficiency, the 4L Gallons Factory promotes the concept of a circular economy. This framework aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible, thereby reducing waste. Instead of following a linear ‘take-make-dispose’ model, the 4L Gallons Factory integrates processes that encourage recycling and repurposing materials. For example, leftover materials from production can be reprocessed into new products, contributing to sustainability and reducing the need for virgin resources.
Furthermore, the promotion of local sourcing within the 4L Gallons Factory model helps bolster local economies and reduces transportation emissions. By prioritizing suppliers who are geographically closer, factories can decrease their logistics-related environmental impact while supporting local businesses. This not only fosters community growth but also reduces the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation.
However, transitioning to a 4L Gallons Factory model is not without challenges. Companies must invest in new technologies and processes, which can be costly. Additionally, staff training and cultural shifts within the organization are necessary to ensure that all employees understand and embrace sustainability initiatives. Despite these hurdles, the long-term benefits, such as cost savings, improved public image, and compliance with regulatory standards, make a compelling case for adopting this model.
In conclusion, the 4L Gallons Factory represents a transformative approach to manufacturing that aligns with the growing demand for sustainability in production. By emphasizing efficient resource use, renewable energy, water conservation, and circular economy principles, this model not only benefits the environment but also promotes economic growth and community development. As global awareness of environmental issues continues to rise, the 4L Gallons Factory may very well serve as a blueprint for the future of sustainable manufacturing, steering industries toward a more responsible and sustainable path.
-
Custom Large Metal Box Manufacturers: Durable & Reliable Solutions
NewsAug.08,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers - Custom & Durable Solutions
NewsAug.07,2025
-
Durable Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | AI-Powered Solutions
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Leading Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Top Steel Pail with Lid Manufacturers | Rust-Proof
NewsAug.03,2025