Oct . 14, 2024 18:32 Back to list
aluminium tin
The Role of Aluminium and Tin in Modern Industry
Aluminium and tin are two metals that play crucial roles in various industries, each with unique properties that make them valuable for different applications. Understanding these metals' characteristics and their significance in current technological advancements is essential for recognizing the future of materials science.
The Role of Aluminium and Tin in Modern Industry
In addition to weight savings, aluminium has excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, which makes it a preferred material for heat exchangers and electrical cables. The rising demand for energy-efficient technologies has further accelerated the use of aluminium in the production of solar panels and batteries. As industries strive towards sustainability, aluminium's recyclability also becomes a key factor, as it can be reused without losing its intrinsic properties, significantly reducing the carbon footprint associated with production processes.
aluminium tin
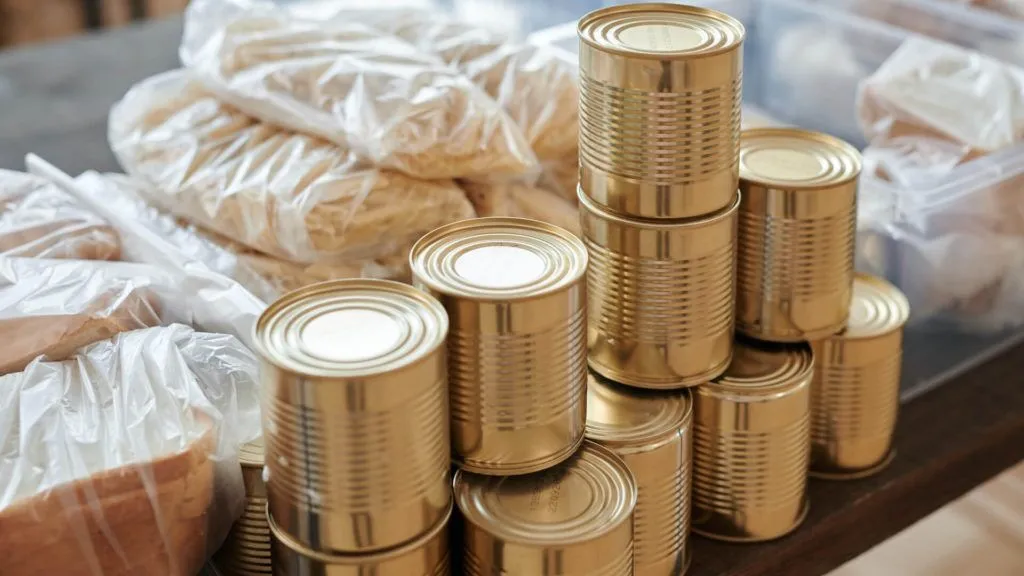

Tin, on the other hand, is often overshadowed by more commonly known metals but is equally important. With its malleability and resistance to corrosion, tin is primarily used for coating other metals to prevent rust and degradation. The most notable application is in tin plating, which involves applying a thin layer of tin onto steel or iron containers, making them ideal for food preservation. This application is crucial in the food packaging industry, ensuring products remain fresh and safe.
Moreover, tin is an essential component in soldering, particularly in the electronics industry. It serves as the main material in lead-free solder, which is crucial for manufacturing electronic devices, from smartphones to computers. As the world transitions towards greener technologies, the demand for tin is expected to increase, given that many new technologies depend on reliable and efficient electronic connections.
The synergy between aluminium and tin is also noteworthy. In some applications, these metals are used in combination to achieve desirable properties. For example, alloying aluminium with tin can enhance its performance in specific industrial applications, such as enhancing wear resistance and reducing friction in mechanical components.
As we look to the future, the ongoing research and development in metallurgy will likely uncover new uses and methods to optimize aluminium and tin's properties. With the increasing emphasis on sustainability and efficiency, these metals will continue to be integral to innovation across various sectors, ensuring that they remain vital components in our industrial landscape.
-
Custom Large Metal Box Manufacturers: Durable & Reliable Solutions
NewsAug.08,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers - Custom & Durable Solutions
NewsAug.07,2025
-
Durable Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | AI-Powered Solutions
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Leading Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.04,2025
-
Top Steel Pail with Lid Manufacturers | Rust-Proof
NewsAug.03,2025