Nov . 07, 2024 17:55 Back to list
Top Manufacturers for Custom 10% Can Dimensions and Packaging Solutions
Understanding the Dimensions of Can Manufacturing A Comprehensive Guide
In the dynamic world of packaging, the dimensions of cans play a crucial role in product appeal, functionality, and feasibility. The can manufacturing industry has evolved significantly over the decades, and understanding the various dimensions and their implications is key for manufacturers, marketers, and consumers alike. This article explores the main aspects surrounding can dimensions and highlights the importance of various manufacturers involved in the process.
The Basics of Can Dimensions
Cans are typically categorized by their diameter and height. The most common can types include aluminum and steel cans, each offering different properties and uses. The dimensions of a can directly influence its capacity, stacking ability, and how well it can be transported and stored.
Manufacturers often describe can dimensions using a standardized nomenclature. For instance, a common specification may include the diameter in millimeters and the height in millimeters, such as a 355 ml can (known for soft drinks) which has a diameter of approximately 66 mm and a height of 124 mm. These measurements determine not only the volume of the liquid it can hold but also its compatibility with automatic filling machines, packaging lines, and shelf displays.
Impact of Can Dimensions on Manufacturing
The manufacturing process is heavily influenced by can dimensions. Different sizes can require distinct production techniques and machinery setups. Standard can sizes are crucial for mass production, allowing manufacturers to streamline operations effectively. However, there's also a growing demand for unique and custom can dimensions to differentiate products in a crowded marketplace.
For example, craft breweries often utilize taller, slimmer cans to convey a premium feel and appeal to their target demographic. Custom dimensions can enhance brand identity but can also present challenges in terms of production costs and logistics. Manufacturers must maintain a balance between meeting market trends and keeping production costs manageable.
The Role of Manufacturers
Several key players in the manufacturing process ensure the production of high-quality cans with precise dimensions. These manufacturers can be classified into two primary categories intermediate and final manufacturers. Intermediate manufacturers typically produce can bodies, while final manufacturers fill the cans with products and seal them.
#10 can dimensions manufacturers
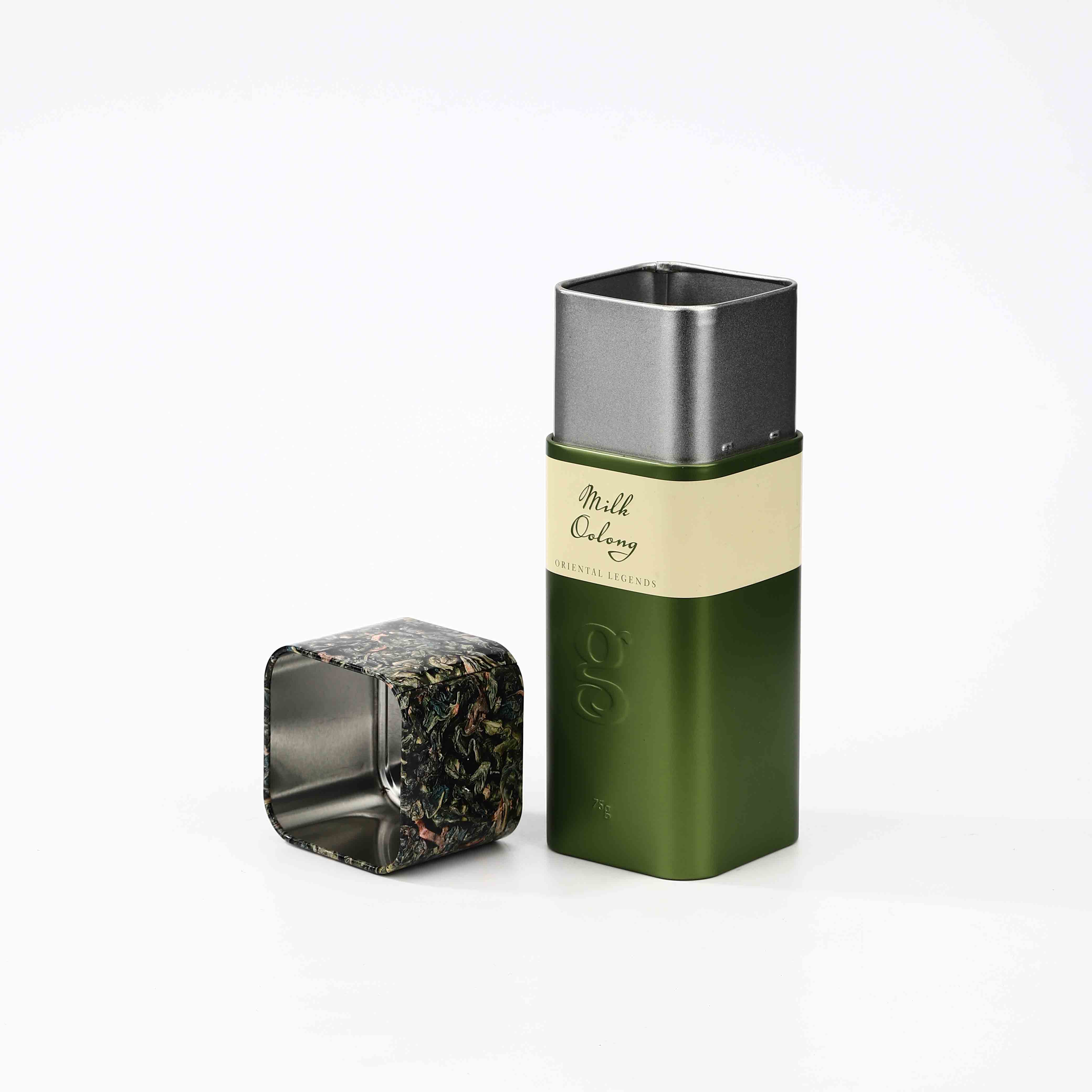

1. Intermediate Manufacturers These companies specialize in producing metal sheets, which are then transformed into can bodies through processes like stamping and welding. Notable manufacturers in this category focus on maintaining rigorous quality control and dimensional accuracy to ensure compatibility in further manufacturing stages.
2. Final Manufacturers These entities fill cans with beverages or food products. They prioritize swift production cycles and efficient packaging solutions, using the dimensions of cans to optimize filling and capping machinery. They also play a significant role in the labeling and branding of cans, where size and shape can impact consumer perception.
Trends Shaping Can Dimensions
Several trends are currently shaping the industry regarding can dimensions
1. Sustainability The move towards eco-friendly packaging has led to the development of lighter cans using less material. This change not only reduces costs but also lessens environmental impact during transport.
2. Consumer Preferences The rise of health-conscious consumers has driven demand for smaller cans in beverages, resulting in a range of sizes catering to different market segments. Manufacturers are constantly adapting to these shifts.
3. Innovative Shapes Unconventional can shapes have emerged, allowing brands to stand out on shelves. Shapes like squared cans or tapered profiles create visual interest and enhance brand recognition, although they may complicate the traditional filling process.
Conclusion
Understanding can dimensions is vital in the manufacturing sector, impacting everything from production efficiencies to consumer preferences. As manufacturers navigate these dimensions, the balance between standardization and customization becomes increasingly critical. By staying attuned to industry trends and evolving consumer demands, can manufacturers can continue to thrive in a competitive landscape. The future of can dimensions promises innovation that aligns with sustainability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal, paving the way for a new era in packaging.
-
Durable Large Metal Boxes | Top Manufacturers & Suppliers
NewsAug.09,2025
-
Custom Large Metal Box Manufacturers: Durable & Reliable Solutions
NewsAug.08,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers - Custom & Durable Solutions
NewsAug.07,2025
-
Durable Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.06,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | AI-Powered Solutions
NewsAug.05,2025
-
Leading Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom Solutions
NewsAug.04,2025