ഫെബ്രു . 02, 2025 02:45 Back to list
large metal box service
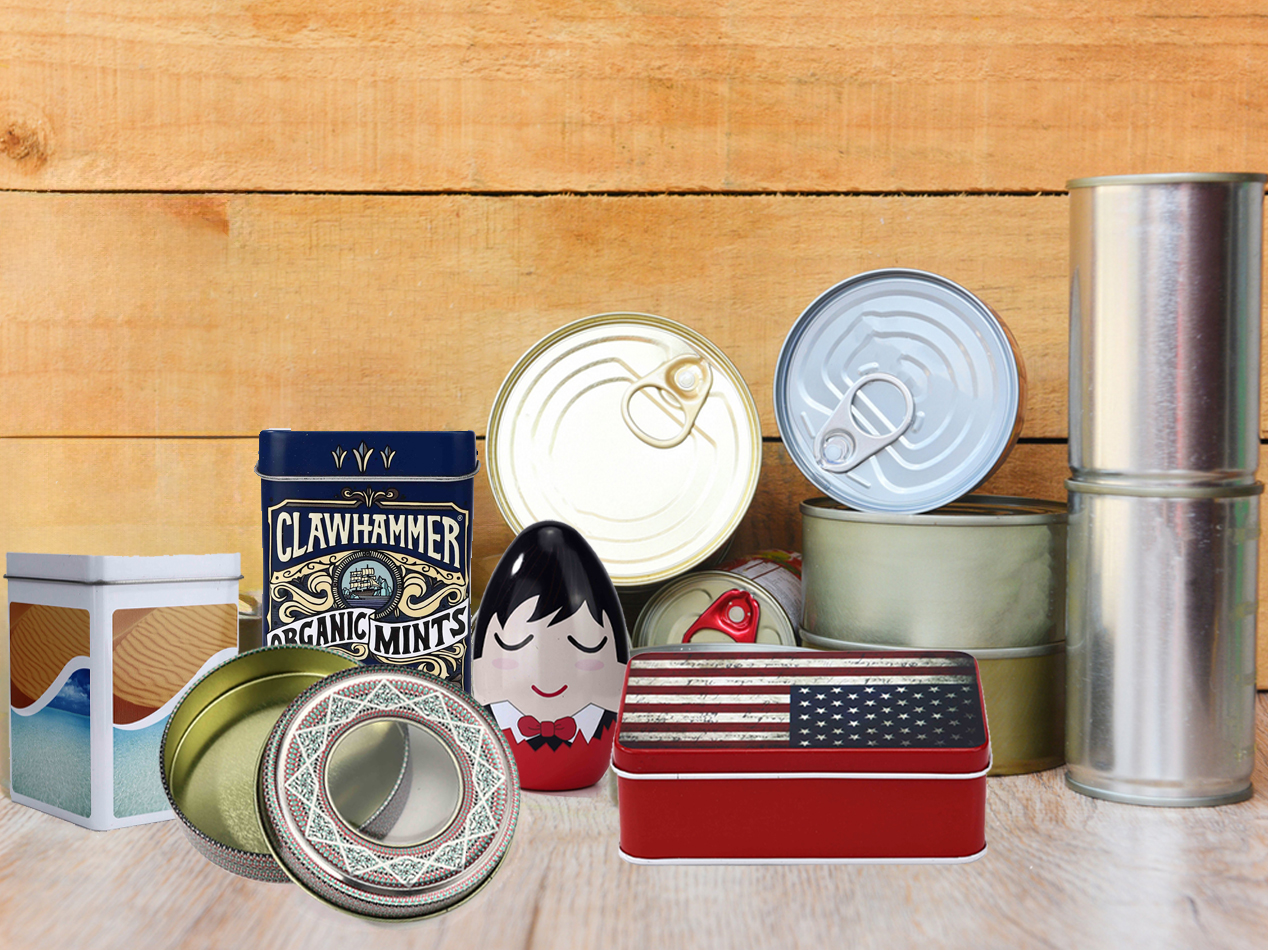
Aluminium and tin are two metals that have increasingly become essential in various industries due to their unique properties and versatile applications. Although they are both found in many of the same areas of manufacturing and production, each metal possesses specific characteristics that make it suitable for distinct uses. With advances in technology and increased demand for sustainable materials, the importance of understanding the differences and synergies between aluminium and tin has become more pronounced.
Despite their differences, aluminium and tin also share common ground as materials pivotal to sustainable development. Both metals can be recycled repeatedly without loss of integrity, a crucial factor in reducing environmental footprint. The growing emphasis on circular economies has bolstered the recycling industry, where both aluminium and tin are seen as cornerstones of environmentally friendly practices. In an era where consumers and businesses alike are increasingly conscious of their environmental responsibilities, understanding the lifecycle and recyclability of materials like aluminium and tin is critical. As the push for green alternatives accelerates, leveraging these metals' sustainable properties will not only enhance product appeal but also reinforce a brand's commitment to sustainability. Companies can gain a competitive edge by highlighting these materials' inherent ecological benefits, positioning themselves as leaders in an ever-evolving market landscape. Furthermore, staying abreast of innovations in the processing and application of these metals ensures competitive superiority. Constant advancements in metal processing technologies, such as 3D printing and nanotechnology, unlock new potential for aluminium and tin applications, offering companies fresh avenues for product development and efficiency improvements. To capitalize on the strengths of aluminium and tin, businesses must foster a nuanced understanding of these materials' properties, exploration of their novel applications, and integration of sustainable practices in their manufacturing processes. By aligning their products and strategies with the growing global focus on sustainability, firms not only meet market demand but also contribute to a more sustainable future. Aluminium and tin, distinct yet complementary, offer untapped possibilities across industries. Their adaptability and sustainability potential make them unparalleled resources for innovation. Firms that invest in understanding and leveraging these metals' unique qualities stand to reap significant benefits, establishing themselves as pioneers in a world increasingly driven by environmental consciousness and technological advancement.


Despite their differences, aluminium and tin also share common ground as materials pivotal to sustainable development. Both metals can be recycled repeatedly without loss of integrity, a crucial factor in reducing environmental footprint. The growing emphasis on circular economies has bolstered the recycling industry, where both aluminium and tin are seen as cornerstones of environmentally friendly practices. In an era where consumers and businesses alike are increasingly conscious of their environmental responsibilities, understanding the lifecycle and recyclability of materials like aluminium and tin is critical. As the push for green alternatives accelerates, leveraging these metals' sustainable properties will not only enhance product appeal but also reinforce a brand's commitment to sustainability. Companies can gain a competitive edge by highlighting these materials' inherent ecological benefits, positioning themselves as leaders in an ever-evolving market landscape. Furthermore, staying abreast of innovations in the processing and application of these metals ensures competitive superiority. Constant advancements in metal processing technologies, such as 3D printing and nanotechnology, unlock new potential for aluminium and tin applications, offering companies fresh avenues for product development and efficiency improvements. To capitalize on the strengths of aluminium and tin, businesses must foster a nuanced understanding of these materials' properties, exploration of their novel applications, and integration of sustainable practices in their manufacturing processes. By aligning their products and strategies with the growing global focus on sustainability, firms not only meet market demand but also contribute to a more sustainable future. Aluminium and tin, distinct yet complementary, offer untapped possibilities across industries. Their adaptability and sustainability potential make them unparalleled resources for innovation. Firms that invest in understanding and leveraging these metals' unique qualities stand to reap significant benefits, establishing themselves as pioneers in a world increasingly driven by environmental consciousness and technological advancement.
Latest news
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Durable Custom Industrial Enclosures
NewsAug.30,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom, Durable Solutions
NewsAug.29,2025
-
Steel Pail with Lid Manufacturers: Durable & Secure Pails
NewsAug.28,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom, Durable & Reliable
NewsAug.27,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom & Durable Industrial Solutions
NewsAug.26,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Custom, Durable Solutions
NewsAug.25,2025