វិច្ឆិកា . 25, 2024 17:41 Back to list
tin boxx factory
The Tin Box Factory A Legacy of Craftsmanship and Innovation
In the bustling world of manufacturing, few industries hold as much charm and nostalgia as the tin box factory. Known for producing a myriad of products ranging from decorative containers to practical storage solutions, a tin box factory is a place where craftsmanship and innovation intersect. This article explores the fascinating world of tin box manufacturing, its historical significance, and its modern-day relevance.
A Brief History of Tin Box Manufacturing
Tin boxes have a rich history that dates back to the 19th century when they were first mass-produced for a variety of purposes. Initially, these boxes were designed to store food items, with the tin coating providing excellent protection against moisture and pests. The popularity of tin boxes soared during the industrial revolution as advances in technology allowed for faster production and cheaper materials. Manufacturers began to experiment with different sizes and designs, leading to the birth of collectible tins adorned with vibrant artwork.
The craftsmanship involved in creating these boxes became an art form, with skilled artisans meticulously shaping, printing, and assembling each piece. The historical significance of tin boxes extended beyond their practical uses; they became symbols of consumer culture, often representing the first containers that families would use to store goods in their homes.
Craftsmanship and Production Process
The tin box factory, often characterized by its rhythmic sounds of machines and the vibrant smell of metal, is a testament to human ingenuity. The production process begins with sheets of tinplate, which are cut into precise shapes and sizes. The cutting process is typically done using advanced machinery, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
tin boxx factory
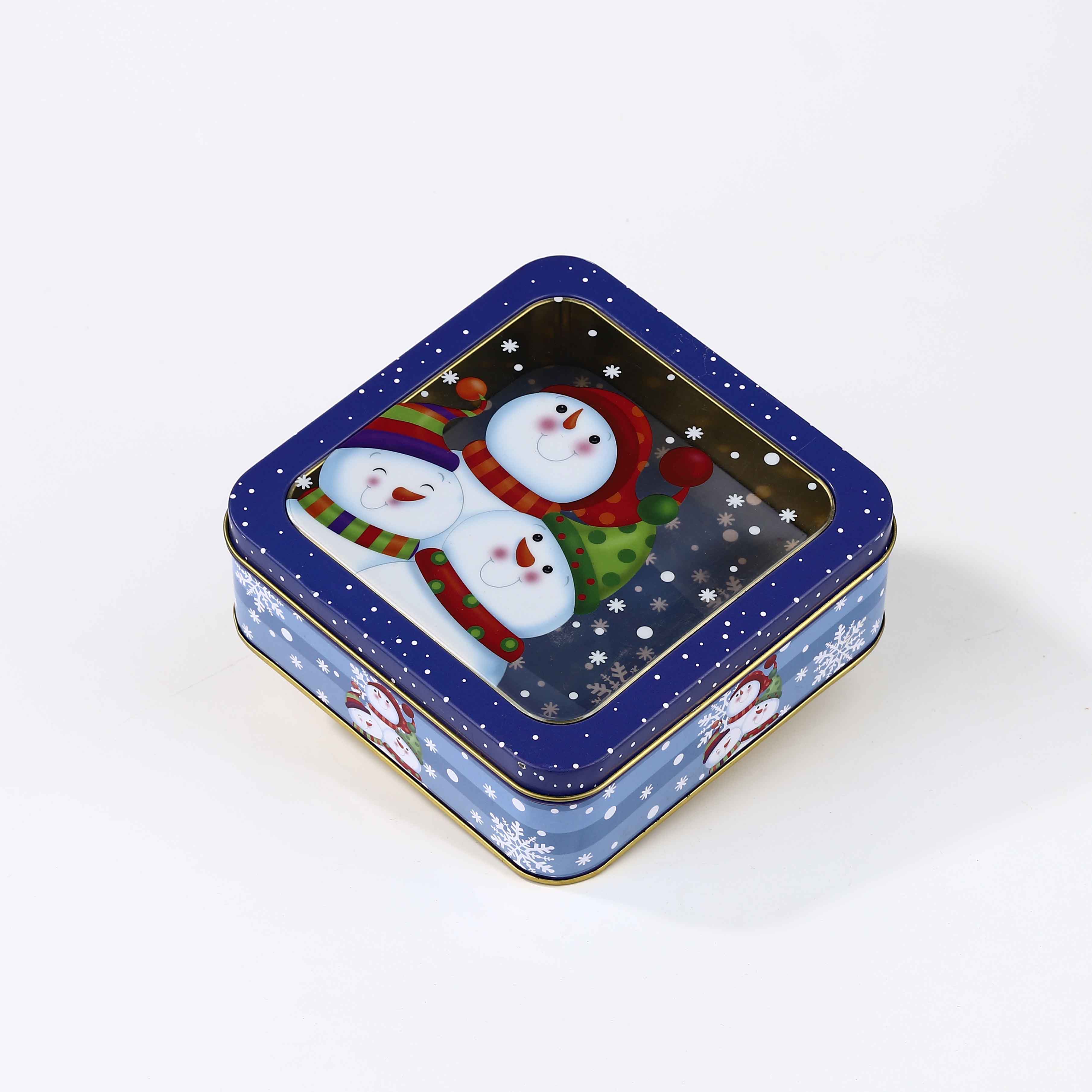

After cutting, the tin pieces are shaped into boxes using a method known as stamping. This process involves pressing the flat tin into molds that form the sides, lids, and base of the box. The stamping process combines precision engineering and careful timing, as the metal must be manipulated while maintaining its structural integrity.
Once the tin pieces are formed, they undergo a rigorous cleaning process to remove any contaminants. After cleaning, the boxes are coated with a protective finish to prevent rust and enhance the visual appeal. This is where the artistry of the factory comes into play; skilled designers create intricate patterns and images, often employing techniques like lithography to transfer artwork onto the surface of the tin.
Modern-Day Challenges and Innovations
In the contemporary era, the tin box factory faces challenges posed by changing consumer demands and the rise of digital manufacturing. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation. With the growing trend toward sustainability, many tin box manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials and manufacturing practices. Recyclability and the use of reclaimed metals have become focal points, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, the appeal of tin boxes has been rejuvenated by their use in promotional campaigns and bespoke packaging. Many brands recognize the nostalgia associated with tin boxes and seek to incorporate them into their marketing strategies, thereby connecting with consumers on a deeper level.
Conclusion
The tin box factory represents a harmonious blend of tradition and modernity. With its roots in historical craftsmanship and its forward-thinking approach to sustainability, the factory continues to hold relevance in a rapidly changing world. Whether it be through packaging, storage, or artistic expression, tin boxes remain a beloved staple that transcends generations. As we look to the future, we can expect the tin box factory to evolve, yet still remain grounded in the rich legacy of creativity and innovation that has defined it for centuries.
-
Top Steel Pail with Lid Manufacturers - Durable & Secure
NewsAug.19,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers: Custom & Durable Solutions
NewsAug.18,2025
-
Durable Large Metal Box Manufacturers & Custom Solutions
NewsAug.17,2025
-
Large Metal Box Manufacturers | Durable & Custom Solutions
NewsAug.16,2025
-
Top Steel Pail with Lid Manufacturers | Durable & Secure Solutions
NewsAug.15,2025
-
Custom Round Cookie Tins Manufacturers | Bulk Supplier
NewsAug.14,2025